What are sodium-ion batteries and how do they compare to lithium-ion batteries?
What is a sodium ion battery? A sodium-ion battery is an electrochemical energy storage device that stores and releases energy by circulating sodium ions between the positive and negative electrodes. It is similar to a lithium-ion battery, but uses sodium ions instead of lithium ions.
In a sodium-ion battery, both the positive and negative electrodes contain sodium compounds. When the battery is charged, the sodium ions move from the positive electrode to the negative electrode and are stored in the void of the negative electrode. When the battery is discharged, the sodium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, releasing energy.
The advantage of sodium-ion batteries over lithium-ion batteries is that sodium is more abundant and cheaper on Earth, thus allowing for lower costs in large-scale applications. Sodium-ion batteries can be used for many applications.
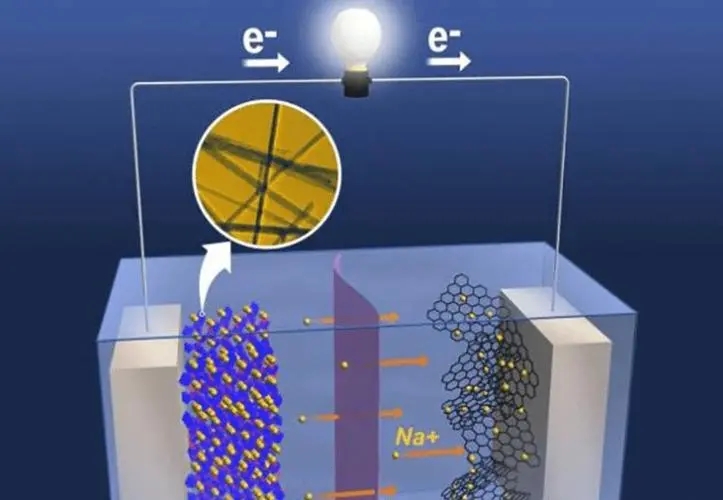
Differences between sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries
There are several major differences between sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries:
1, Chemical reaction: sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries have different chemical reaction mechanisms. In sodium-ion batteries, the positive and negative electrodes of the battery contain sodium compounds, while in lithium-ion batteries it is lithium compounds. During the charging and discharging process, sodium ions and lithium ions circulate and move inside the battery, storing and releasing energy through redox reactions.
2, Energy density: sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries have different energy densities. Although the storage capacity of sodium is higher than that of lithium, sodium-ion batteries have a lower energy density relative to lithium-ion batteries. This means that sodium-ion batteries require more space to store the same amount of energy.
3, Low tempearture discharge performance: The normal operating temperature range of sodium-ion batteries is -40°C-80°C, and the capacity retention rate of some products can reach 88% at -20°C, which is significantly better than lithium iron phosphate with 60-70% capacity retention rate.
4, Cost: Since sodium is more abundant and cheaper on earth, sodium-ion batteries are less costly compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Overall, sodium-ion batteries and lithium-ion batteries have their own advantages and disadvantages, and should be selected according to specific application scenarios. Sodium-ion batteries have advantages in large-scale applications and long-term cycle life, while lithium-ion batteries are more superior in terms of energy density and volume.

 简体中文
简体中文 Russian
Russian French
French German
German Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Spanish
Spanish





