Why are energy storage systems important? What are its benefits?
Affected by different times of the year or climates, solar and wind power do not always generate electricity when energy is needed most, and energy storage is an indispensable technology for accelerating the replacement of fossil fuels with renewable energy. Peak electricity use typically occurs in the summer afternoons and evenings, when solar generation is dropping but temperatures aren't, and people come home from work and start using electricity to cool their homes, cook their meals and run other appliances.
As the share of renewable energy in the grid continues to grow, energy storage systems will play an increasingly critical role between renewable energy supply and electricity demand response. Energy storage systems can be deployed in the same place as solar and wind power generation systems, or they can be located at a considerable distance from the new energy generation system, with the storage system being stand-alone. Either way, it helps to integrate new energy sources into the overall energy landscape. In this way, even if there is no big sun, energy storage can help solar energy to contribute to the power supply.
The energy storage system mentioned above, or battery energy storage system (BESS), is a device that can store electricity generated from renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, and release it when the demand for energy is greatest.
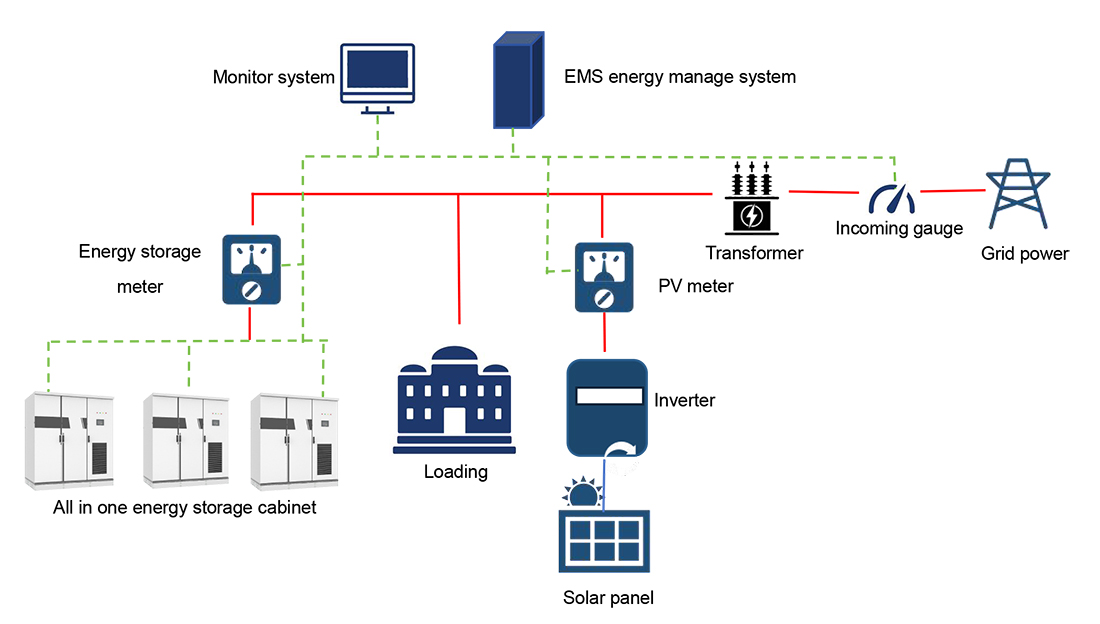
Lithium-ion batteries are the primary electrical energy storage technology currently used in mobile electronic devices and electric vehicles, as well as the primary technology used in large power plants to ensure a reliable supply of renewable energy to the grid. Batteries are used for energy storage in addition to storage at the power generation end, energy storage systems for industrial, commercial and residential buildings.
Why are energy storage systems important and what are their benefits?
Energy storage system technology plays a key role in ensuring that homes and businesses have access to green energy, even when the sun doesn't shine or the wind stops blowing.
For example, the UK has the largest installed offshore wind capacity in the world, and capturing wind energy and deploying it purposefully can add value to clean energy, with scale potentially reducing costs. Every day, power engineers in the UK's National Grid and globally must balance supply and demand. Peak and valley management becomes even more challenging when the goal is to achieve zero carbon production. Traditionally, coal-fired generation has been used to regulate peaks and valleys, but battery storage facilities can gradually replace some of the coal-fired peaking generators. The UK government estimates that technologies like energy storage systems, which support the integration of more low-carbon power, heat and communications technologies, could save the UK energy system up to £40 billion ($48 billion) by 2050, thereby ultimately reducing people's energy bills.

Energy storage technologies can further facilitate the development of renewable energy, both from an operational and stable power supply perspective, and can also drive the continued development and shift of utilities to renewable energy.
How do battery energy storage systems work?
Battery energy storage systems are far more advanced than the batteries you keep in a drawer or in your child's toy. Battery storage systems are primarily recharged using electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
Smart battery software uses algorithms to coordinate the production of electricity, and a computer control system is used to determine when energy is stored or released into the grid. At times of peak power usage, the battery storage system releases energy, reducing costs and keeping power available.
While large storage systems are discussed here, our household storage systems follow the same principles.
Other Renewable Energy Storage Options
Storing renewable energy requires a battery that has a long life, can be charged and discharged thousands of times, is safe and reliable, and can cost-effectively and efficiently store enough energy to meet demand.
Lithium-ion batteries were developed by a British scientist in the 1970s and were first used commercially by Sony in 1991 in the company's portable video recorders. While currently the most economically viable energy storage solution, there are many other energy storage technologies under research and development. These include:
Pumped storage: pumped storage utilizes excess electricity to pump water to an elevated reservoir, and when energy is needed, electricity is generated by releasing the water flow to drive a turbine generator. Pumped storage is a long-tested and proven energy storage technology, but the value of pumped storage for integrating the services of unstable renewable energy sources has not yet been fully realized, with the exception of energy arbitrage.
Compressed air energy storage: These systems are usually located in large chambers, e.g. large ships or natural caves consisting of excess electricity used to compress air and store it. When energy is needed, the compressed air is released and electricity is generated via an air turbine. Existing compressed air energy storage systems typically use the released air as part of a natural gas power cycle to generate electricity.
Mechanical Gravity Energy Storage: An example of this type of system uses energy to lift concrete blocks up a tower. When energy is needed, the concrete blocks are lowered and gravity is used to generate electricity.
Flow batteries: In these batteries, chemical energy is supplied by two chemical components dissolved in a liquid within the system and separated by a membrane.
The most common type of energy storage in power grids is pumped storage hydroelectricity, which is now widely used in power systems. However, the energy storage technologies most often combined with solar power plants and wind farms are battery storage and thermal fluid storage with protection of the power plant. Other types of energy storage, such as compressed air storage and flywheel storage, may have different characteristics, such as very fast discharges or very large capacities, making them attractive for grid operators as well.
Grid instability is increasing due to the addition of large amounts of new energy sources, new loads and smart power electronics. The next decade will thus be very important for energy storage, especially for batteries, as it will be an important validation period for various battery and other technologies.

 简体中文
简体中文 Russian
Russian French
French German
German Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Spanish
Spanish





